In each pair of compounds, which compound has the higher boiling point? Explain your reasoning.
c. 2,2,5-trimethylhexane or nonane
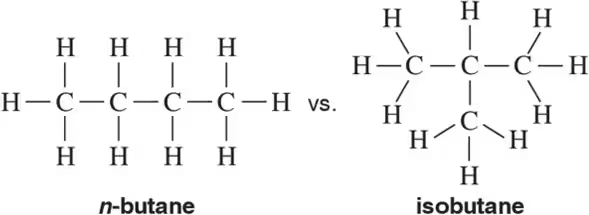
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: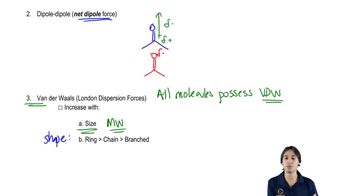


 3:08m
3:08mMaster How IMFs are related to melting and boiling points. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning