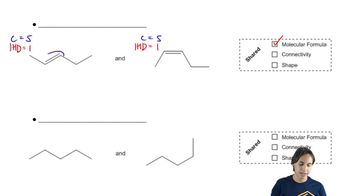
Predict the product(s) that would result when the alkenes are allowed to react under the following conditions: (ix) H2, Pd/C; and (x) D2, Pd/C.
(f)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 5:21m
5:21mMaster General properties of catalytic hydrogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning