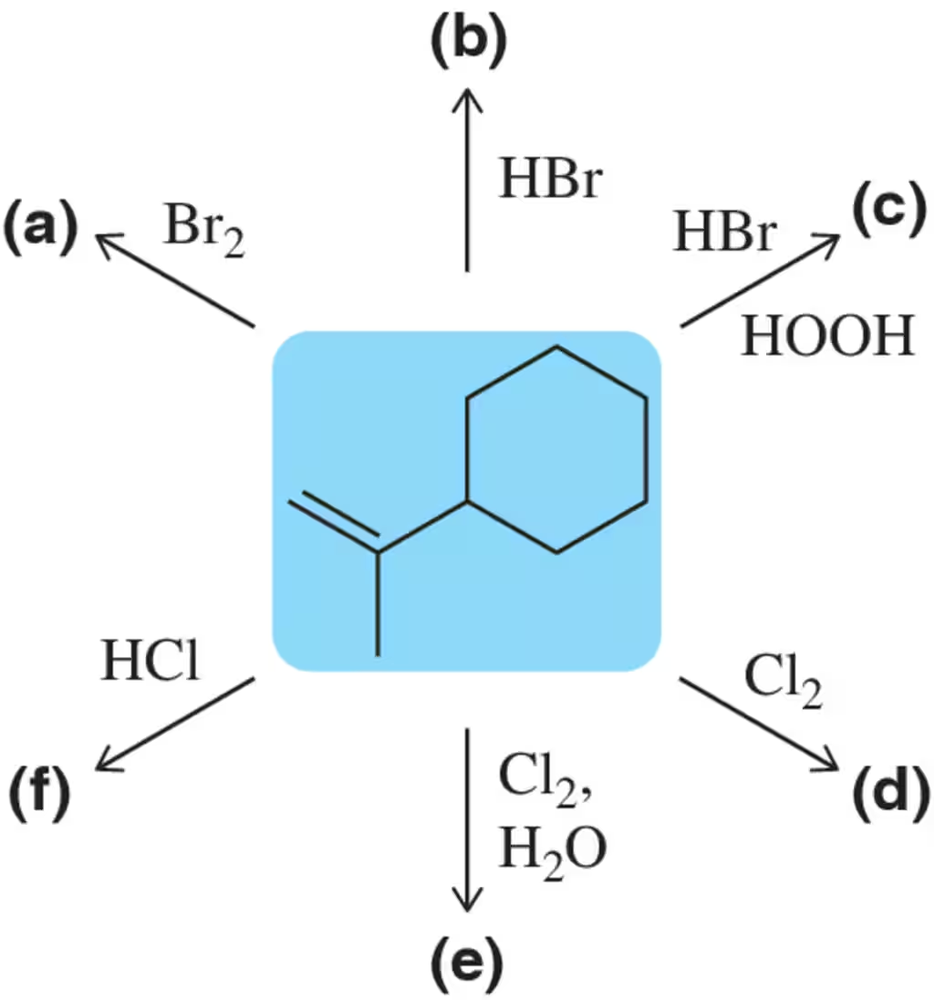
(a) Based on what you know about the relative stabilities of alkyl cations and benzylic cations, predict the product of addition of HBr to 1-phenylpropene.
(b) Propose a mechanism for this reaction.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: