What is the major product of the reaction of each of the following with HBr?
c.
d.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: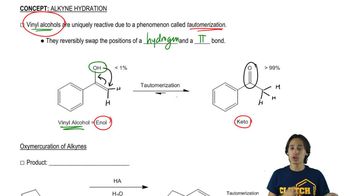
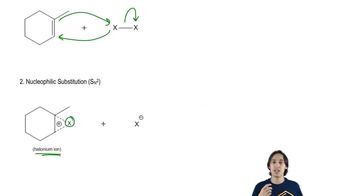

 4:07m
4:07mMaster General properties of hydrohalogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning