Textbook Question
When 3-methyl-1-butene reacts with HBr, two alkyl halides are formed: 2-bromo-3-methylbutane and 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. Propose a mechanism that explains the formation of these two products.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: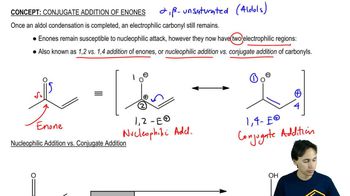


 4:07m
4:07mMaster General properties of hydrohalogenation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning