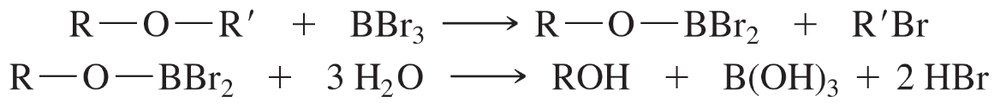
Textbook Question
Suggest a mechanism by which TXB2 might be formed from TXA2 in an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction. [The structure has been simplified.]
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 4:22m
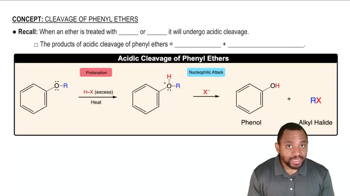
4:22mMaster How to predict the products of Ether Cleavage. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning