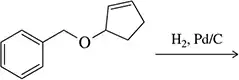
Boron tribromide (BBr3) cleaves ethers to give alkyl halides and alcohols.
The reaction is thought to involve attack by a bromide ion on the Lewis acid–base adduct of the ether with BBr3 (a strong Lewis acid). Propose a mechanism for the reaction of butyl methyl ether with BBr3 to give (after hydrolysis) butan-1-ol and bromomethane.