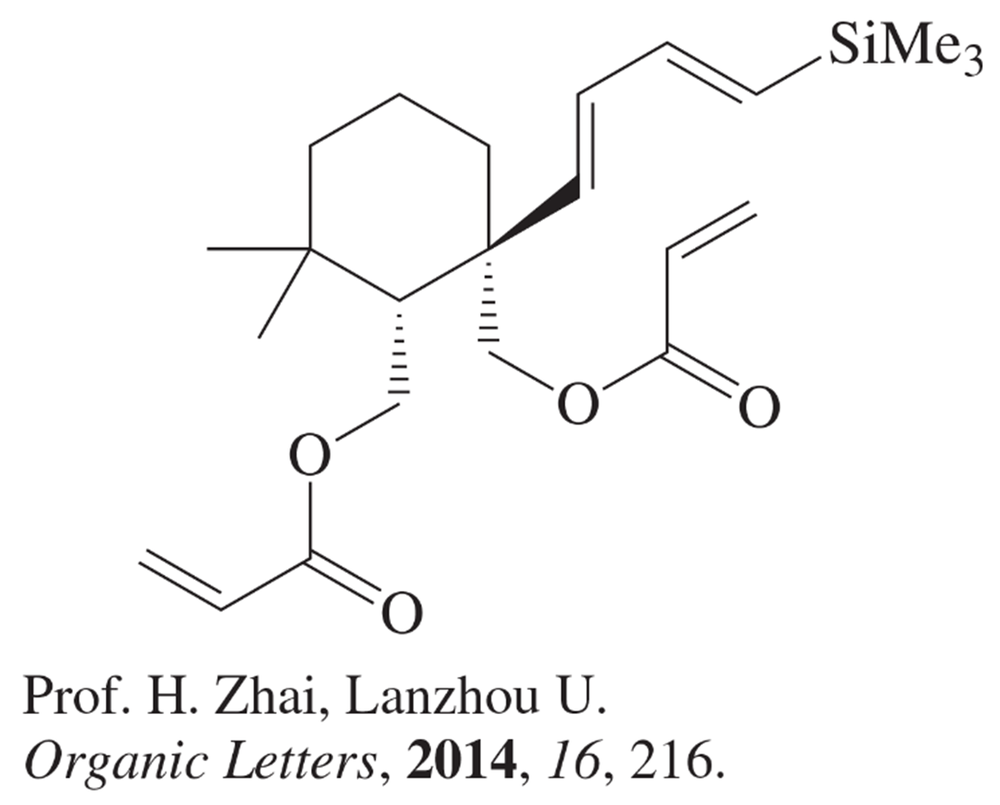
An important variation of the Diels–Alder reaction is intramolecular, in which the diene and the dienophile are connected. This type of Diels–Alder reaction makes two new rings. Draw the compound produced in each of these examples; try to predict stereochemistry (using models will help). In some cases, Lewis acid catalysts are used; that can be ignored for this problem.
(a)
(b)