For each horizontal row of substituted benzenes, indicate
c. the one that yields the highest percentage of meta product in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
3.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: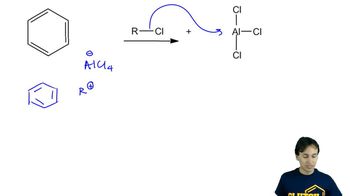
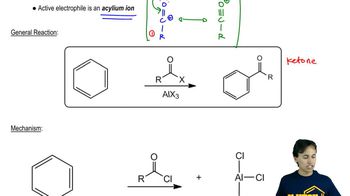
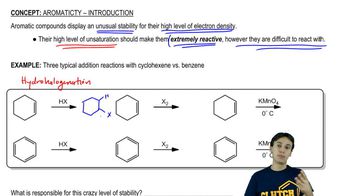

 4:29m
4:29mMaster Activity and Directing Effects with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning