Using an alkyl halide and a thiol as starting materials, how would you prepare the following thioethers?
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: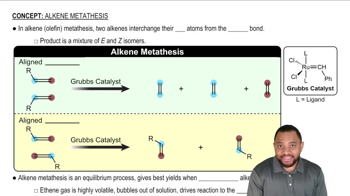


 3:21m
3:21mMaster The mechanism of Sulfide Synthesis. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning