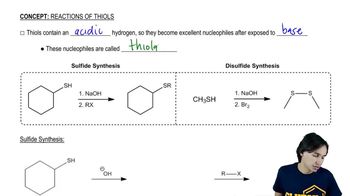
(a) Show how you would synthesize the pure (R) enantiomer of 2-butyl methyl sulfide, starting with pure (R)-butan-2-ol and any reagents you need
(b) Show how you would synthesize the pure (S) enantiomer of the product, still starting with (R)-butan-2-ol and any reagents you need.