Draw the product formed when each of the following compounds undergoes an electrocyclic reaction
b. under photochemical conditions.
1.
2.
![Chemical structure diagram illustrating a [2 + 2] cycloaddition reaction yielding two possible products under light exposure.](https://static.studychannel-dev.pearsondev.tech/courses/organic-chemistry/thumbnails/a1aef2df-e7dd-4462-9820-3d2aa7482f26)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: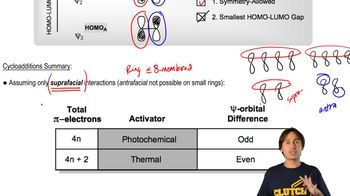
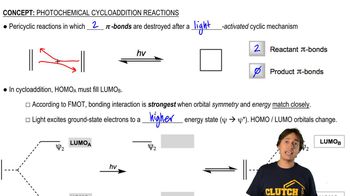


 4:49m
4:49mMaster MO Theory of Photochemical Electrocyclics with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning