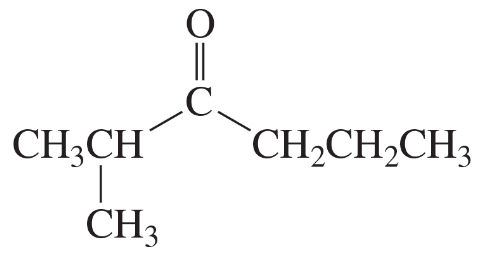
Predict the multiplicity (the number of peaks as a result of splitting) and the chemical shift for each shaded proton in the following compounds.
(a)
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: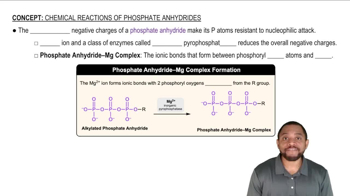

 12:21m
12:21mMaster Splitting without J-values with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning