For the following acid–base reactions studied in Assessment 5.25, draw a likely transition state. Be sure to indicate in your drawing the degree to which bonds are broken or formed.
(c) H3O+ + Br– ⇌ H2O + HBr
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: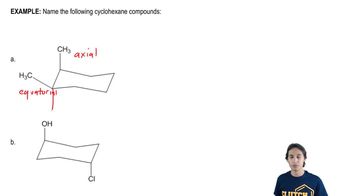

 5:02m
5:02mMaster Breaking down the different terms of the Gibbs Free Energy equation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning