Draw the predominant form for glutamate in a solution with the following
pH: b. 3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
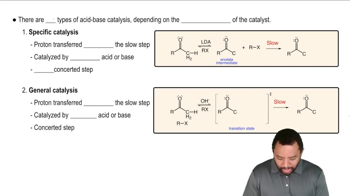
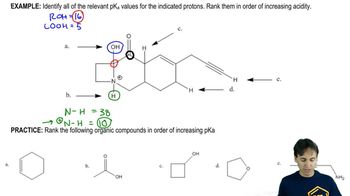
Verified video answer for a similar problem: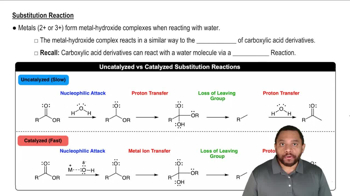

 4:41m
4:41mMaster Why Amino Acids Exist as Zwitterions with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning