Draw the structure and give the systematic name for a compound with molecular formula C5H12 that has
(c) one tertiary hydrogen
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: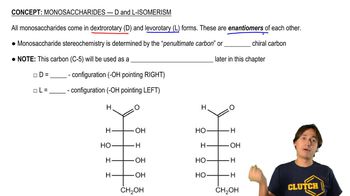
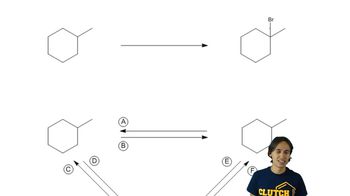
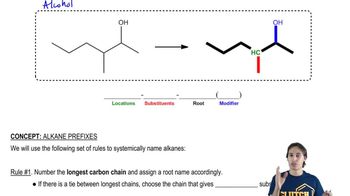

 3:43m
3:43mMaster The different parts of an IUPAC name with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning