Identify the following dienes as being in the s-cis or s-trans conformation. If they are in the s-trans conformation, draw them in the s-cis conformation. [It may not always be possible.]
(e)
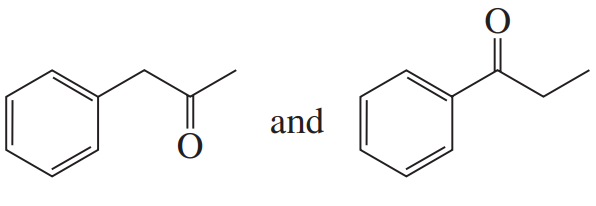
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:29m
5:29mMaster Definition of Conjugation with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning