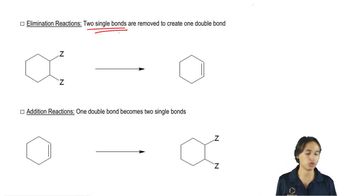
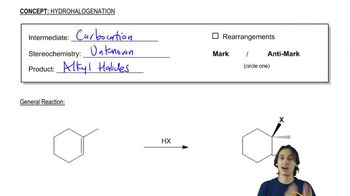
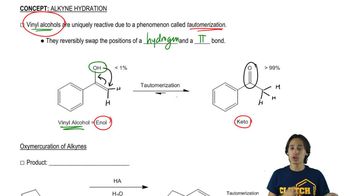
a. Starting with 3-methyl-1-butyne, how can you prepare the following alcohols?
2. 3-methyl-1-butanol
b. In each case, a second alcohol would also be obtained. What alcohol would it be?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: