Textbook Question
a. Show the reagents required to form the primary alcohol in each of the following reactions.
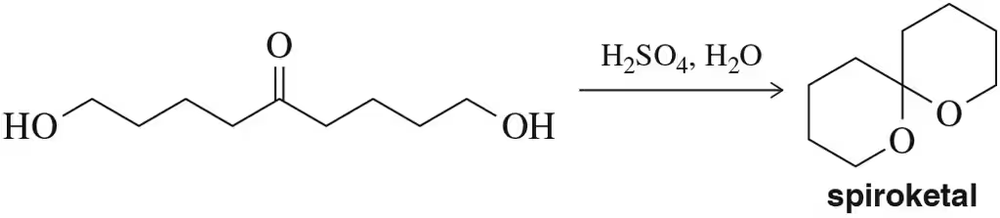
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: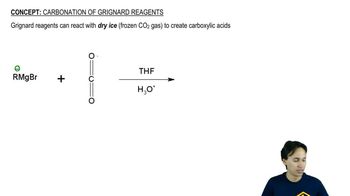

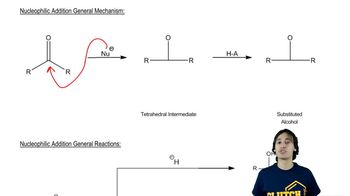

 2:26m
2:26mMaster Forming alcohols through Oxymercuration-Reduction. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning