Hydration of alkynes (via oxymercuration) gives good yields of single compounds only with symmetrical or terminal alkynes. Show what the products would be from hydration of each compound.
b. hex-2-yne
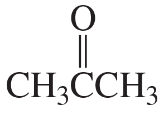
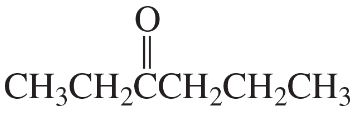
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: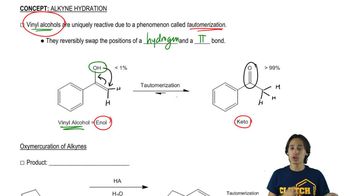

 3:51m
3:51mMaster Vinyl alcohols yield tautomers. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning