Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(c) oct-1-yne
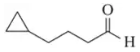
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: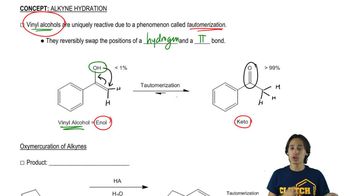
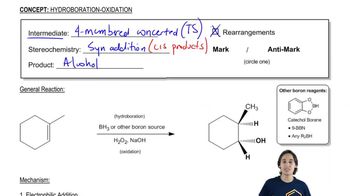

 3:51m
3:51mMaster Vinyl alcohols yield tautomers. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning