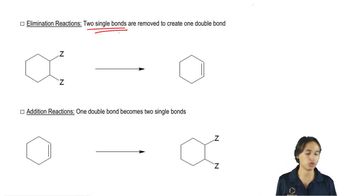
A small amount of another organic product is formed in a Williamson ether synthesis. What is this product when the alkyl halide used in the synthesis of butyl propyl ether is
a. propyl bromide?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: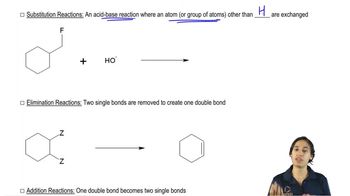


 2:27m
2:27mMaster Overview of the flowchart. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning