Indicate whether an alcohol (ROH) with a pKa value of 15 has more charged or more neutral molecules in a solution with the pH values given in Problem 41.
1. pH = 1
2. pH = 3
3. pH = 5
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: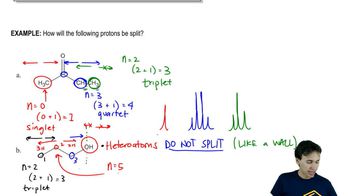
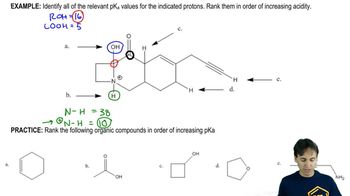


 1:46m
1:46mMaster Why we use pKa instead of pH. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning