Multiple Choice
Provide the correct names and mechanisms for the following sigmatropic shifts
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: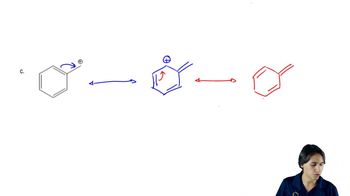
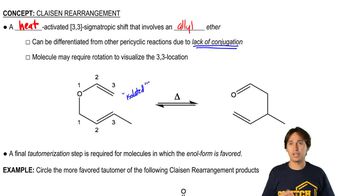
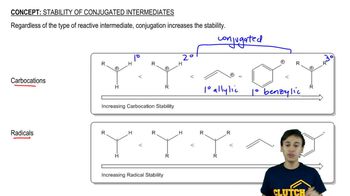

 3:51m
3:51mMaster Definition of Sigmatropic Shifts with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning