For each of the reactions in Problem 15, indicate which reactant is the nucleophile and which is the electrophile.
a.
b.
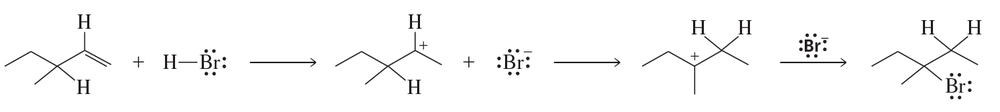
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:14m
5:14mMaster How to tell if a molecule will be reactive or not. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning