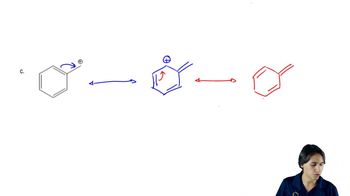
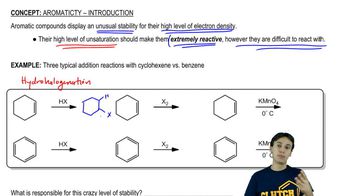
The following molecules and ions are grouped by similar structures. Classify each as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. For the aromatic and antiaromatic species, give the number of pi electrons in the ring.
(g)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: