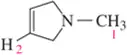
Which underlined proton (or sets of protons) has the greater chemical shift (that is, the higher frequency signal)?
a.
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: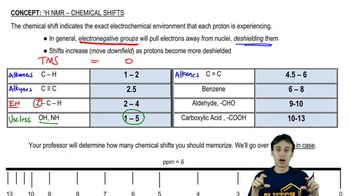
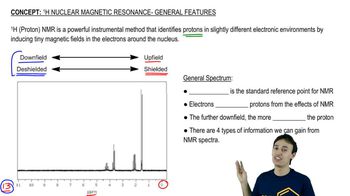


 11:44m
11:44mMaster 1H NMR Chemical Shifts with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning