Textbook Question
Show what product would result from the [6 + 2] cycloaddition of hexa-1,3,5-triene with maleic anhydride.
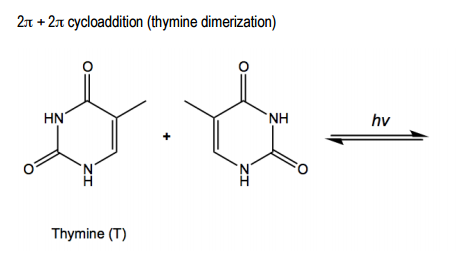

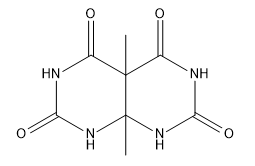
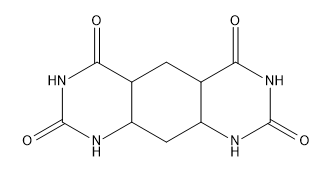
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
 9:36m
9:36mMaster MO Theory of Photochemical Cycloadditions with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning
