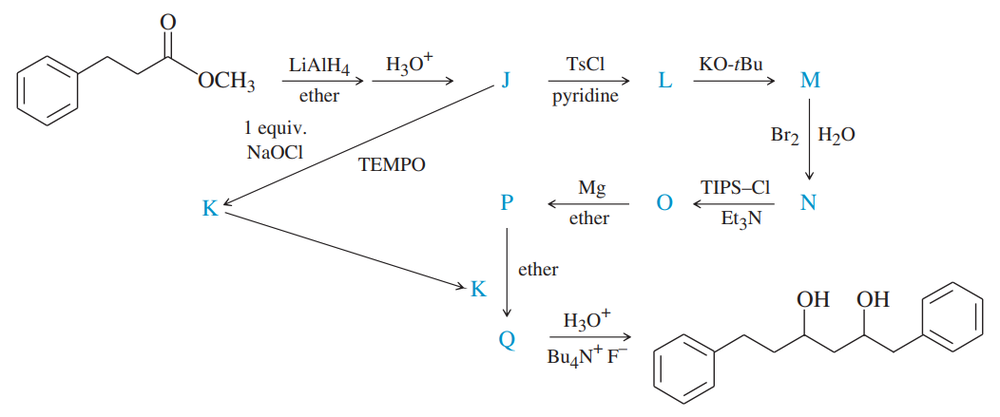
Predict the products you expect when the following starting material undergoes oxidation with an excess of each of the reagents shown below.
d. DMSO and oxalyl chloride
e. DMP (periodinane) reagent
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: