Draw the products, including their configurations, obtained from the reaction of 1-ethylcyclohexene with the following reagents:
c. R2BH/THF, followed by HO–, H2O2, H2O
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: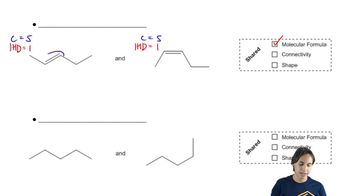

 6:38m
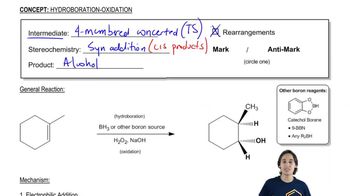
6:38mMaster General properties of hydroboration-oxidation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning