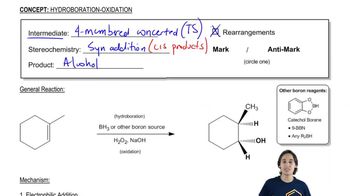
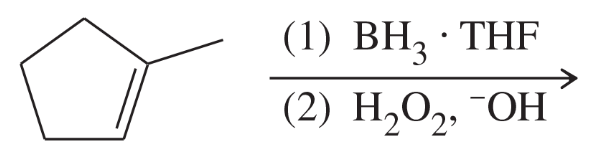Draw the product or products that will be obtained from the reaction of cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene with each of the following reagents. If a product can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed.
2. BH3/THF, followed by HO-, H2O2, H2O