Which occurs at a larger wavenumber:
a. the C–O stretch of phenol or the C–O stretch of cyclohexanol?
b. the C=O stretch of a ketone or the C=O stretch of an amide?
c. the C–N stretch of cyclohexylamine or the C–N stretch of aniline?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: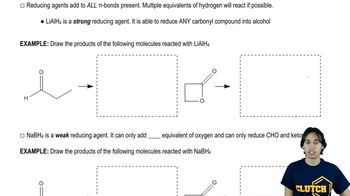

 16:4m
16:4mMaster General Features of IR Spect with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning