From the following rate constants, determined at five temperatures, calculate the experimental energy of activation and ∆G‡, ∆H‡, and ∆S‡ for the reaction at 30 °C:
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: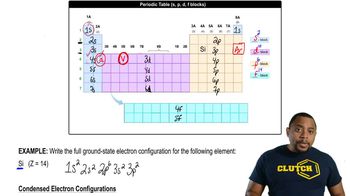


 2:46m
2:46mMaster Explaining what entropy is. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning