For each molecular formula, represent all constitutional isomers using line-angle drawings.
(c) C4H10
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: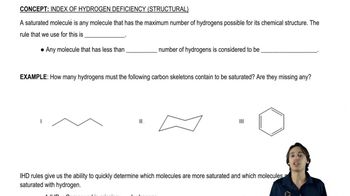

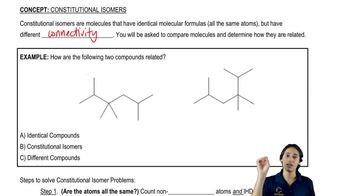

 2:39m
2:39mMaster The difference between saturated and unsaturated molecules. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning