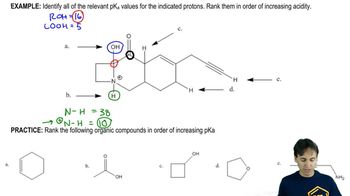
Predict which member of each pair will be more soluble in water. Explain the reasons for your answers.
(a) hexan-1-ol or cyclohexanol
(b) heptan-1-ol or 4-methylphenol
(c) 3-ethylhexan-3-ol or octan-2-ol
(d) hexan-2-ol or cyclooctane-1,4-diol
(e)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: