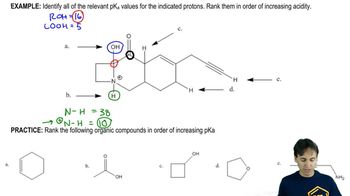
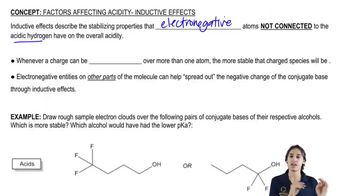
Predict which member of each pair has the higher boiling point, and explain the reasons for your predictions.
a. hexan-1-ol or 3,3-dimethylbutan-1-ol
b. hexan-2-one or hexan-2-ol
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: