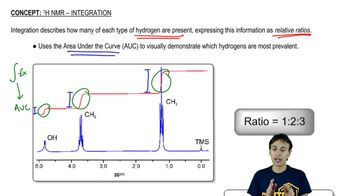
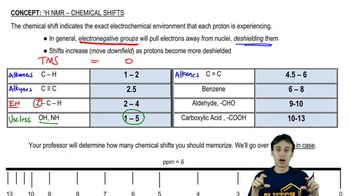
Identify each of the following compounds from the 1H NMR data and molecular formula:
b. C8H9Br: a 3H doublet at 2.01 ppm a 1H quartet at 5.14 ppm
a 5H broad singlet at 7.35 ppm
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: