Which of the following carbocations would you expect to rearrange? If you expect rearrangement, draw the carbocation you expect to form and the mechanism by which it will form.
(f)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: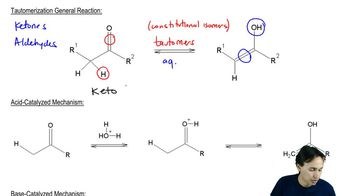
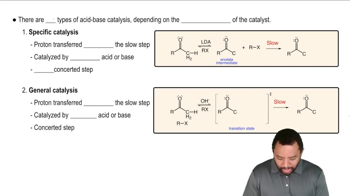
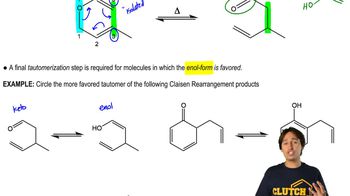

 0:47m
0:47mMaster Understanding why carbocations shift. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning