Rank the following elements from least electronegative to most electronegative.
Na, Si, F, Mg, C, O, N
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: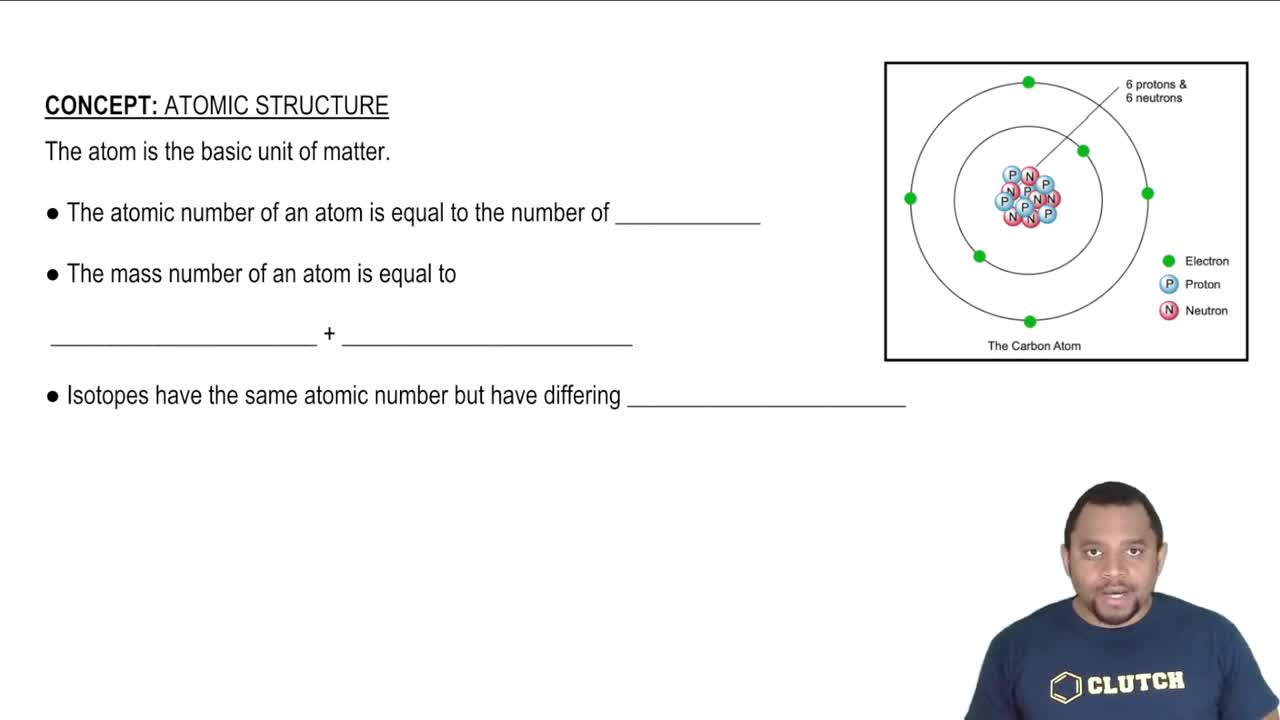


 11:33m
11:33mMaster Differences between ionic, polar and covalent bonds with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning