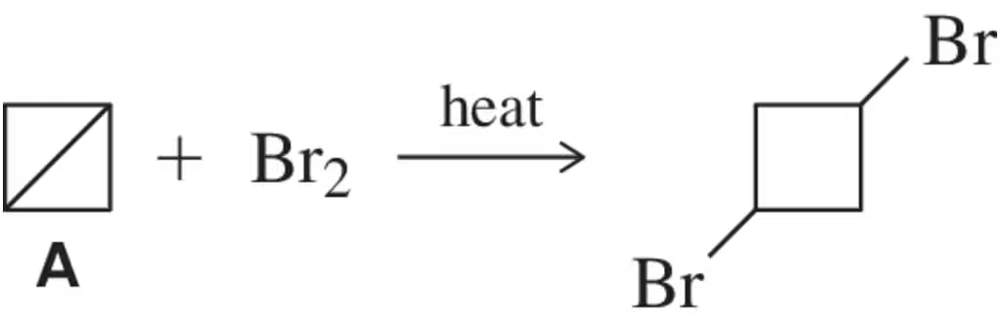
Predict the product(s) of the following halogenation reactions. Only one equivalent of the halogen is used in each case. If the reaction proceeds selectively, indicate this by only drawing the major product. If the reaction is not selective, draw all possible products.
(e)