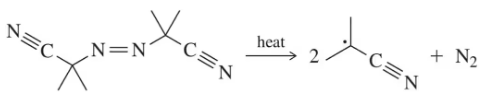
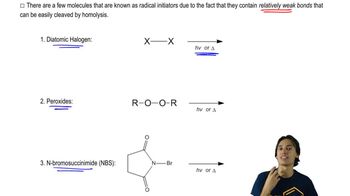
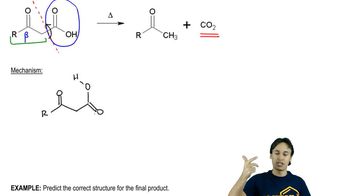
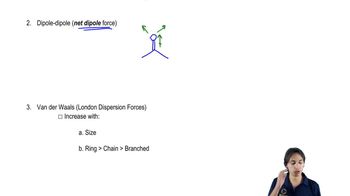
We have studied the following reactions in previous chapters. For each, (i) indicate which reaction sheets they should appear on, (ii) show the best structure to use to represent them, and (iii) write the notes you could put in the margin so that the mechanism is implied.
(b) Radical halogenation of an alkane