Textbook Question
Explain why the enantiomers of 1,2-dimethylaziridine can be separated even though one of the “groups” attached to nitrogen is a lone pair.
<IMAGE>
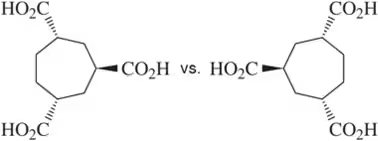
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:41m
5:41mMaster Understanding Other Chiral Atoms with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning