Rank the following alcohols from strongest to weakest acid.
CH2═CHCH2OH; CH3CH2CH2OH; HC≡CCH2OH
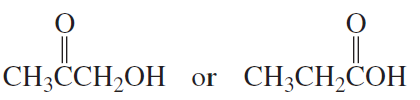
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 3:15m
3:15mMaster Why we need factors affecting acidity and when to use them. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning