A student was given the structural formulas of several compounds and was asked to give them systematic names. How many did the student name correctly? Correct those that are misnamed.
k. 2-methyl-2-isopropylheptane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: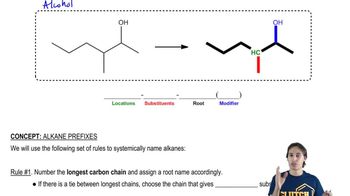


 3:43m
3:43mMaster The different parts of an IUPAC name with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning