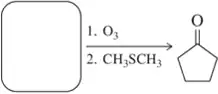
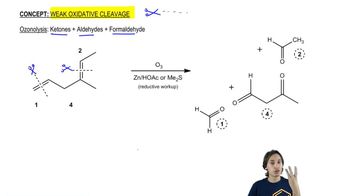
When compound Z is treated with ozone, followed by dimethyl sulfide and washing with water, the products are formic acid, 3-oxobutanoic acid, and hexanal.
Propose a structure for compound Z. What uncertainty is there in the structure you have proposed?