Limonene is one of the compounds that give lemons their tangy odor. Show the structures of the products expected when limonene reacts with an excess of each of these reagents.
(c) ozone, then dimethyl sulfide
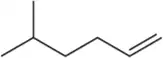
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: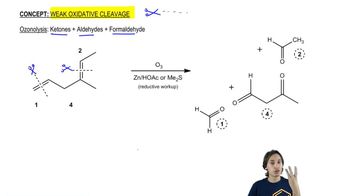
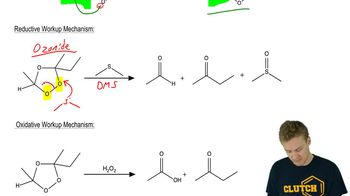

 6:30m
6:30mMaster General properties of ozonolysis. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning