Purine is a heterocyclic compound with four nitrogen atoms.
a. Which nitrogen is most apt to be protonated?
b. Which nitrogen is least apt to be protonated?
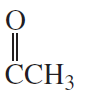
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: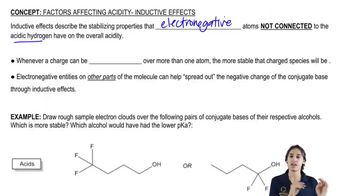

 3:15m
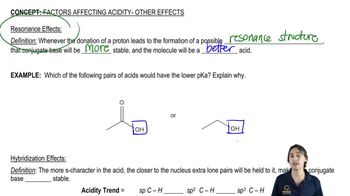
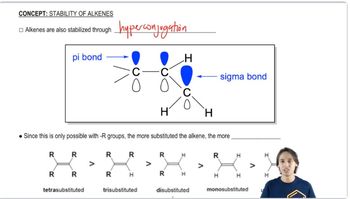
3:15mMaster Why we need factors affecting acidity and when to use them. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning