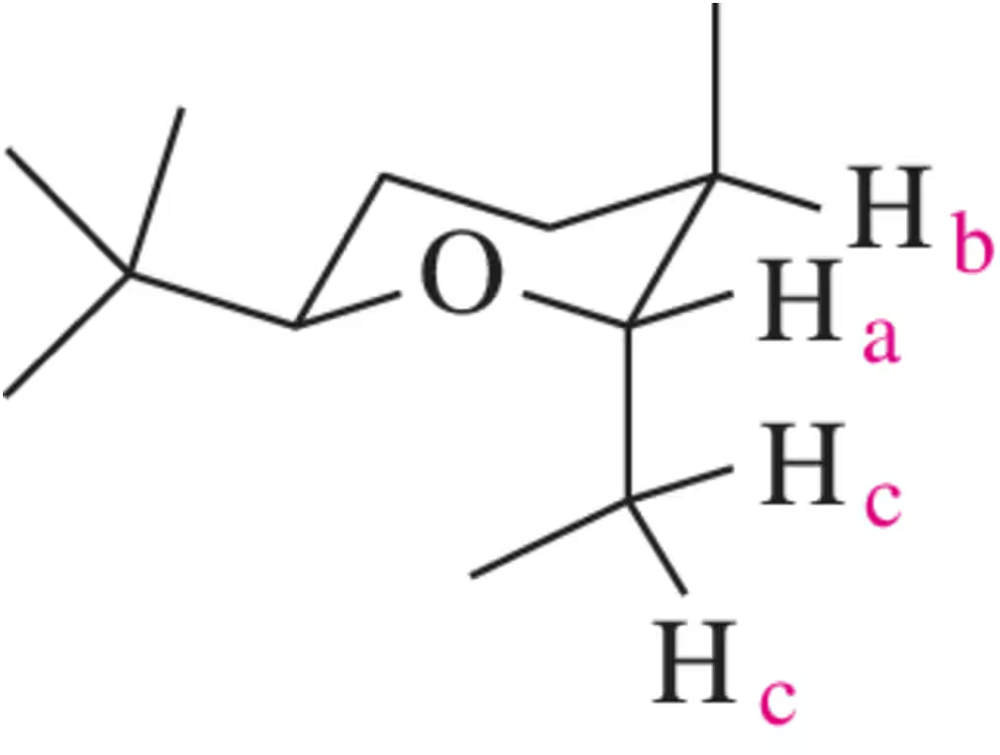
For the hydrogen(s) screened in blue, draw the signal you would expect to see in a ¹H NMR spectrum. At which chemical shift would the signal appear?
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

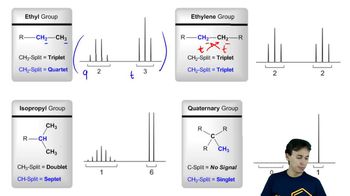

 11:3m
11:3mMaster Splitting with J-Values:Simple Tree Diagram with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning