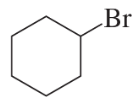
A graduate student attempted the following reaction and did not isolate the expected product.
(a) What product did they isolate?
(b) What reagent should they have used instead to get their desired product?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:30m
4:30mMaster Comparing and contrasting the Alcohol Conversions. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning