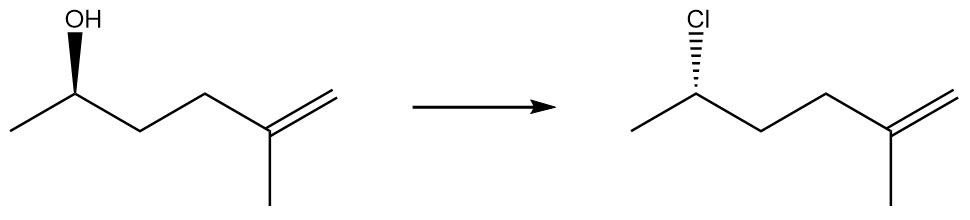
Show how you would convert (S)-hexan-2-ol to
(a) (S)-2-chlorohexane.
(b) (R)-2-bromohexane.
(c) (R)-hexan-2-ol.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 4:30m
4:30mMaster Comparing and contrasting the Alcohol Conversions. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning